[tx_row]
[tx_column size=”1/2″]Drone aerial photography uses unmanned aerial vehicles as aerial platforms, equipped with remote sensing devices such as lightweight optical cameras, infrared scanners, laser scanners, and magnetometers to capture information. This information is then processed by computers to produce images according to certain accuracy requirements. The technology offers advantages such as high clarity, large scale, small area coverage, high timeliness, compactness, and efficient mobility. The takeoff and landing of drones are less restricted by the environment, making them suitable for locations like playgrounds, roads, or other open areas.
Their stability and safety are commendable, and they are easy to transport. They are widely used in areas like national ecological and environmental protection, mineral resource exploration, and natural disaster monitoring and assessment, indicating a vast market demand. This article mainly introduces the application of drone aerial photography in constructing 3D models.[/tx_column]
[tx_column size=”1/2″]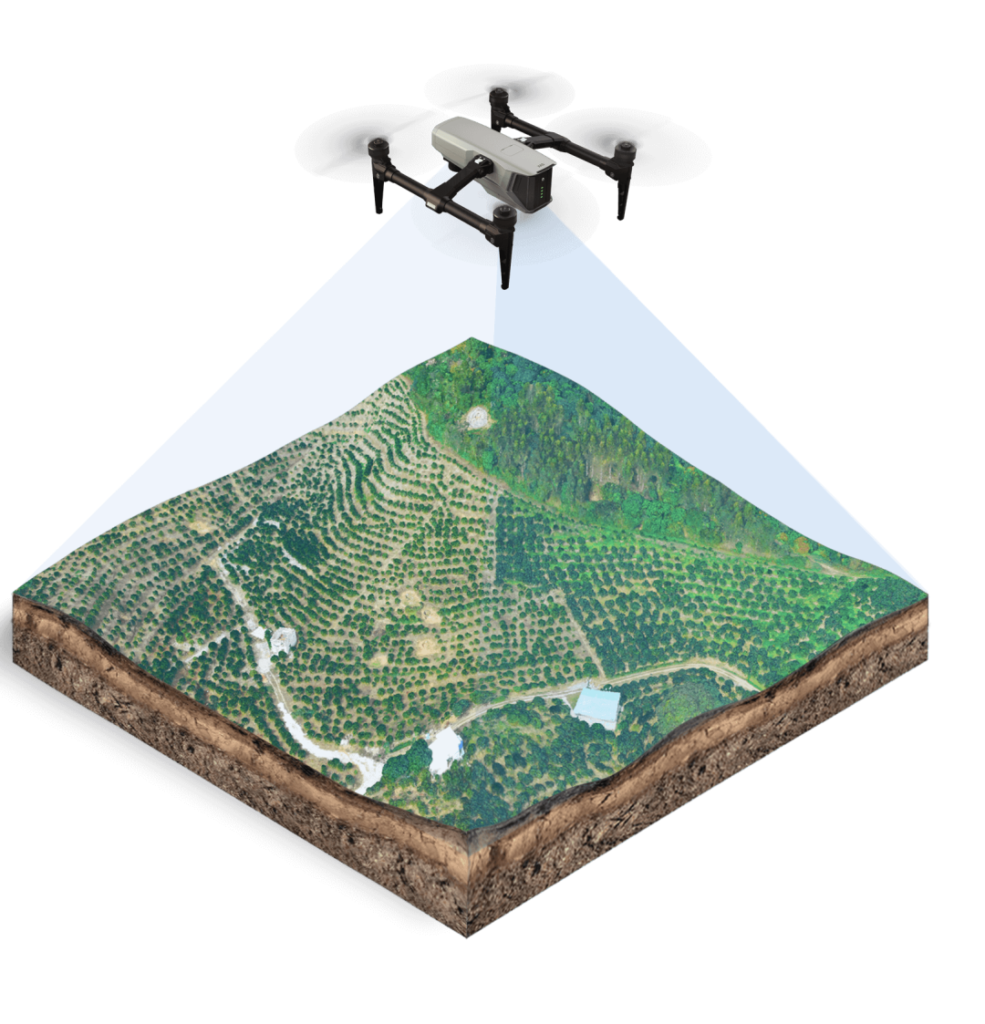 [/tx_column]
[/tx_column]
[/tx_row]
Precautions Before, During, and After Using Drones:
- Before Using Drones:
- (1) Collect data on the flight area. Before operating a drone in special areas (like airports), gather on-site data to ensure its completeness, accuracy, and timeliness, ensuring that it doesn’t interfere with the normal operations of the flight area.
- (2) Conduct on-site surveys in advance if necessary. Understand the tall buildings, high-voltage lines, etc., in the flight area that might affect the drone’s flight and check the location and preservation of existing control points.
- (3) Submit airspace applications. Drone aerial photography should follow the “Basic Flight Rules of the People’s Republic of China.” Depending on the specific conditions of the flight area, flight plans should be submitted to the airspace management department of the aerial survey area before starting the aerial survey task.
- (4) Check the drone’s battery level before the flight.
- (5) Choose favorable weather conditions, avoiding factors like snow, sandstorms, and strong winds that might negatively impact modeling. During aerial photography, there should be sufficient light while avoiding excessive shadows.
- During Drone Use:
- (1) When flying manually, ensure the overlap of photos. The overlap in the flight direction and the lateral overlap should both be more than 75{dadd650eeaba6f64f533239c6790b4fc98b2e0cf5f68cfe74cb088220b8d2ab8} to ensure the quality of subsequent 3D modeling.
- (2) The drone’s takeoff and landing area should be away from high-voltage lines and tall buildings.
- (3) During the aerial survey, once the drone flies over the highest obstacle in the area, it can enter automatic flight. In case of unexpected situations, stay calm, terminate the task promptly, switch to manual control, and ensure the safety of personnel and equipment to the maximum extent.
- After Using Drones:
- (1) After completing the flight task, visually inspect and check for defects in the images. Check for any obvious blurring, double images, or errors at the turning points of the flight path. If there are obvious bad images or missing images in the flight path, retake them under the same weather conditions.
- (2) Check whether the POS data is complete and normal, ensuring that the POS points correspond to the images.
- (3) Conduct model accuracy analysis and error analysis.
3D Modeling Methods
- Oblique Photogrammetry: This technique captures images from five different angles, allowing for rapid and efficient collection of measurement data. Key technologies include multi-view image joint adjustment, digital surface model generation, and true orthophoto correction.
- Modeling Software: Commonly used software includes ContextCapture, Pix4D, and PhotoScan. ContextCapture produces the best 3D model results, Pix4Dmapper is more suitable for surveying and mapping, and PhotoScan is excellent for generating high-quality 3D models from overlapping images.
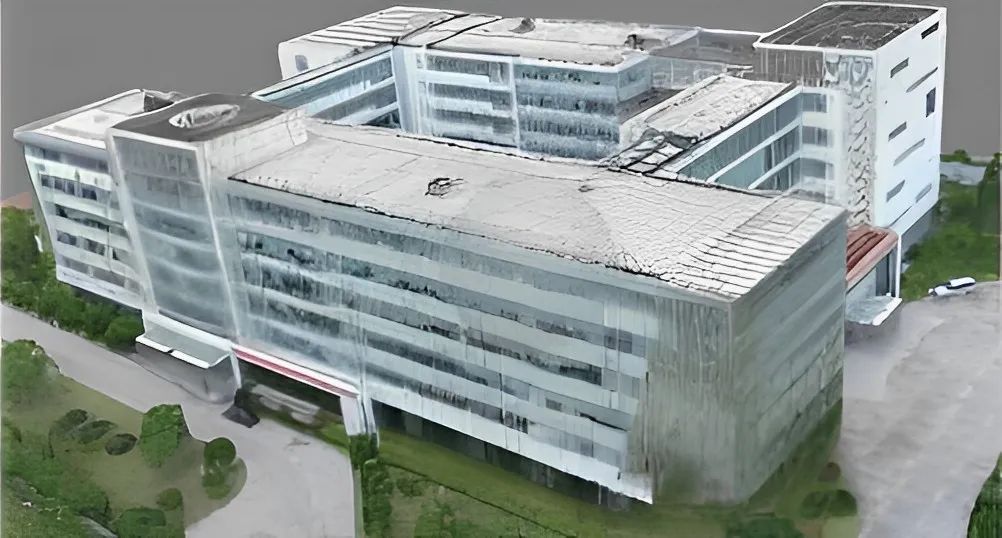
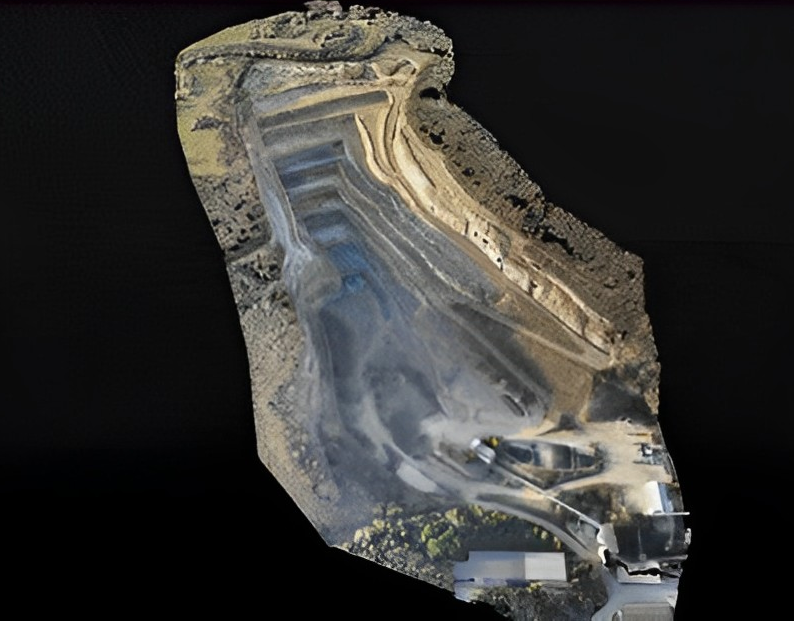


Image Data Processing Workflow
After obtaining image data using drones, the subsequent data processing workflow includes:
- Aerial triangulation of oblique images to obtain high-precision external orientation elements.
- Dense matching of multi-view images to obtain a high-density 3D point cloud.
- Texture mapping based on the 3D TIN model.
- Output to obtain a true 3D model of the city.
Application Examples
Various researchers have applied drone oblique photogrammetry in fields like geological exploration, mine ecological restoration, and ancient architectural 3D reconstruction. The technology not only digitalizes outcrops but also serves as a reliable tool for geologists conducting efficient field investigations.
Applications in Geological Exploration
In geological exploration, drone oblique photogrammetry can be used to capture high-resolution images of outcrops, providing a clear view of rock structures, fractures, and other geological features. These images can be processed to create detailed 3D models, which can be further analyzed to understand the geological history and evolution of the area.
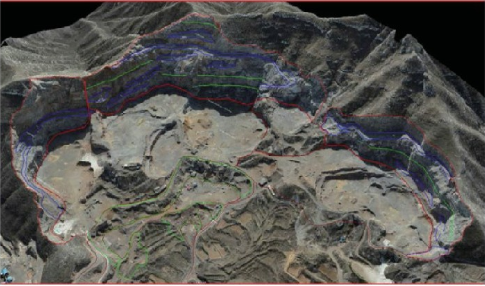
In the field of mine ecological restoration, drones can be used to monitor the progress of restoration efforts. By capturing images of the mine area at regular intervals, researchers can track changes in vegetation cover, soil erosion, and other ecological indicators. The 3D models created from these images can be used to assess the effectiveness of restoration measures and guide future efforts.
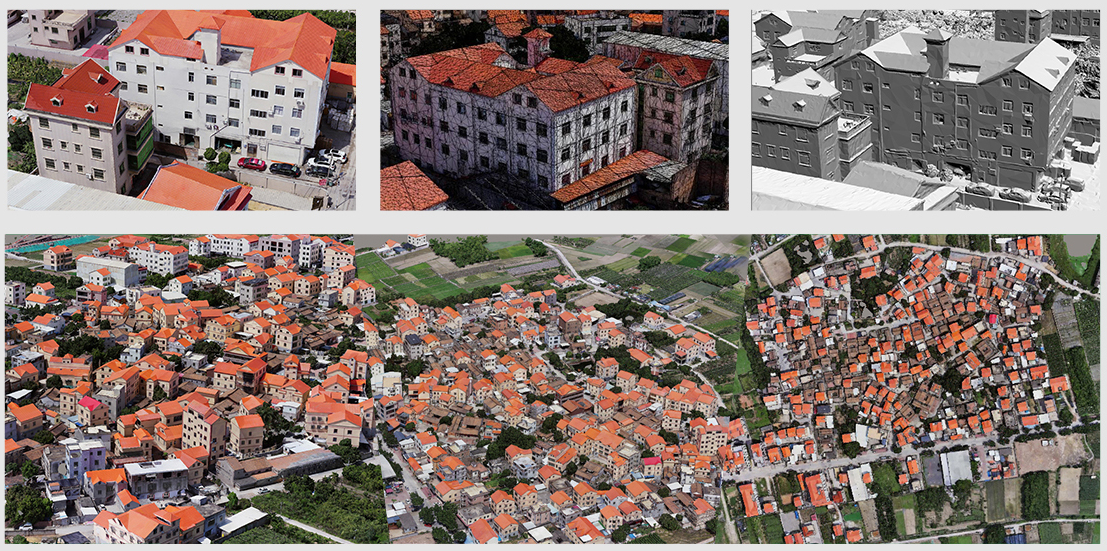
Applications in Ancient Architectural 3D Reconstruction
Drones have also been used in the field of cultural heritage preservation. By capturing images of ancient buildings and structures, researchers can create detailed 3D models that provide valuable insights into the architectural techniques and styles of the past. These models can be used for restoration and preservation efforts, ensuring that these cultural treasures are preserved for future generations.

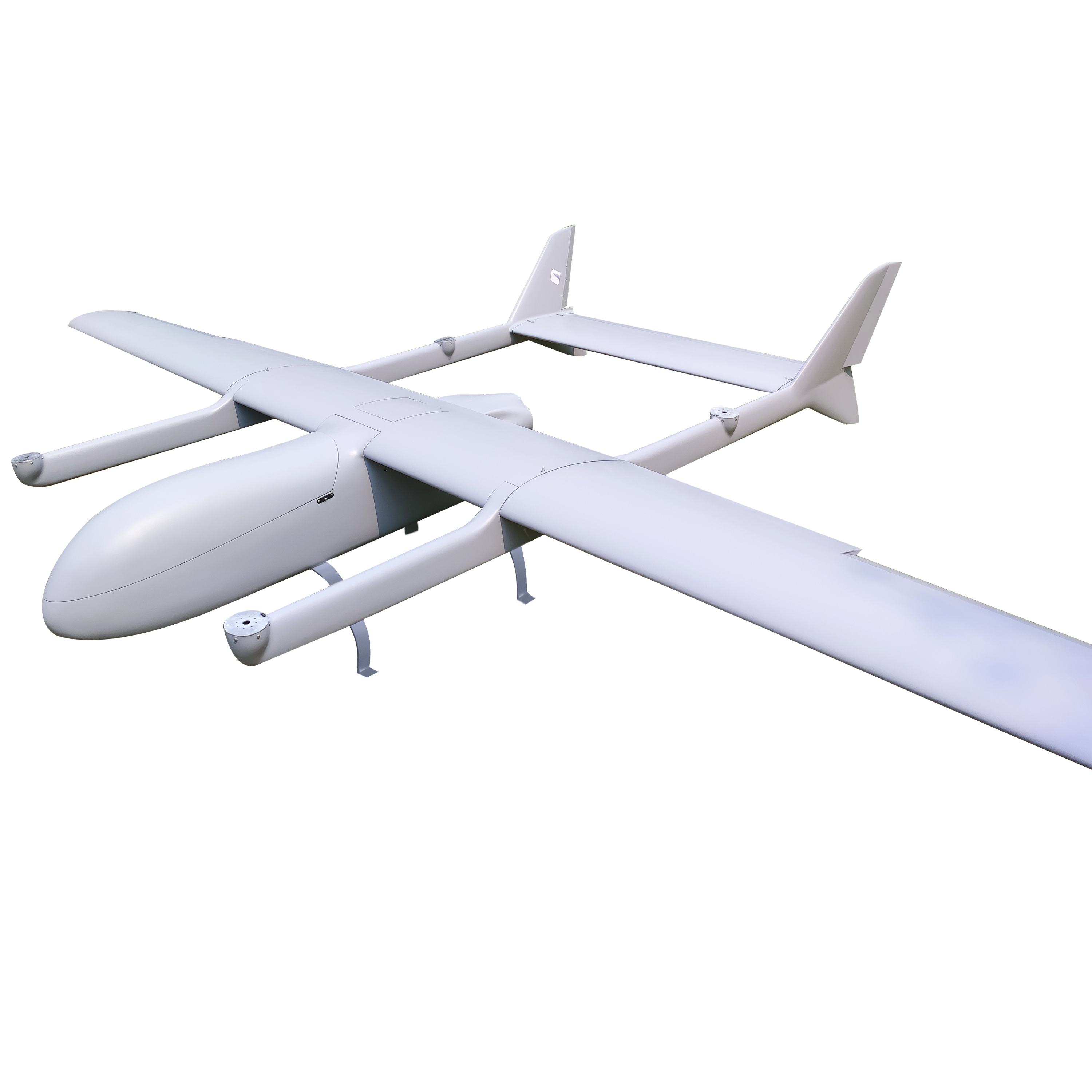
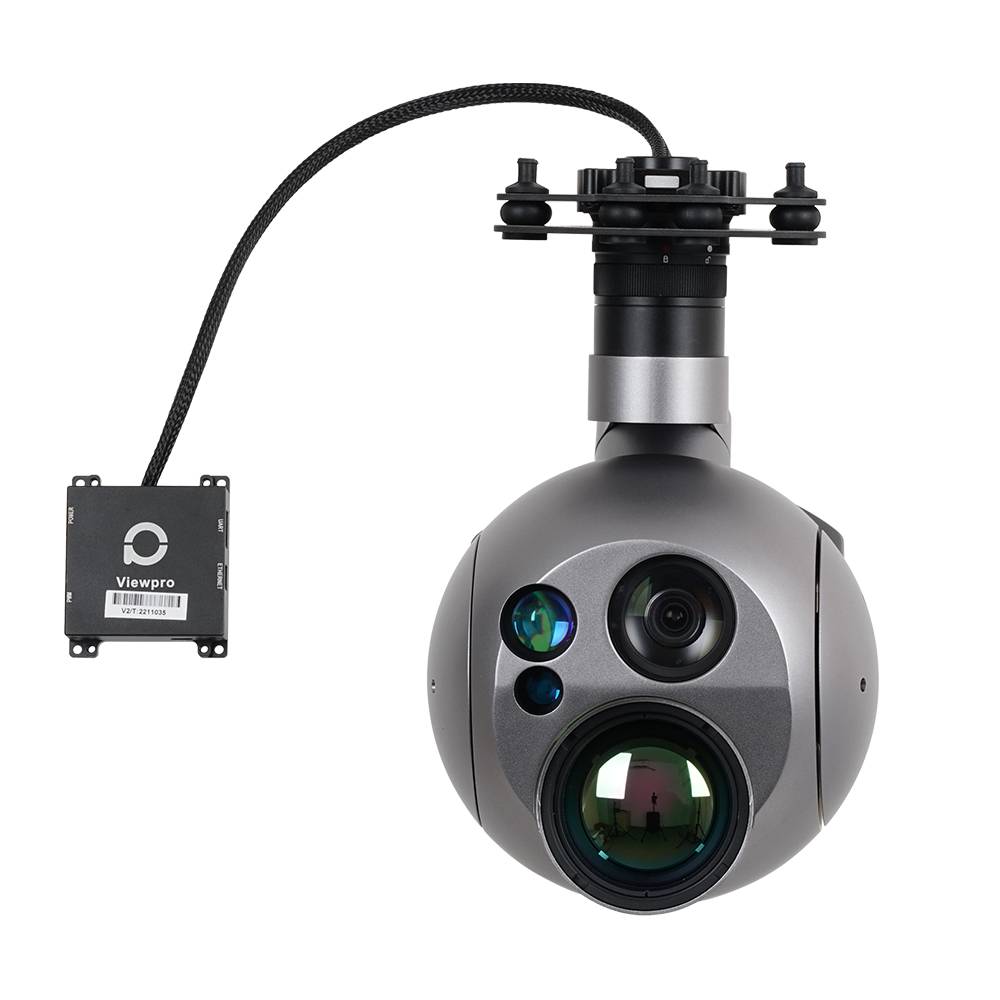
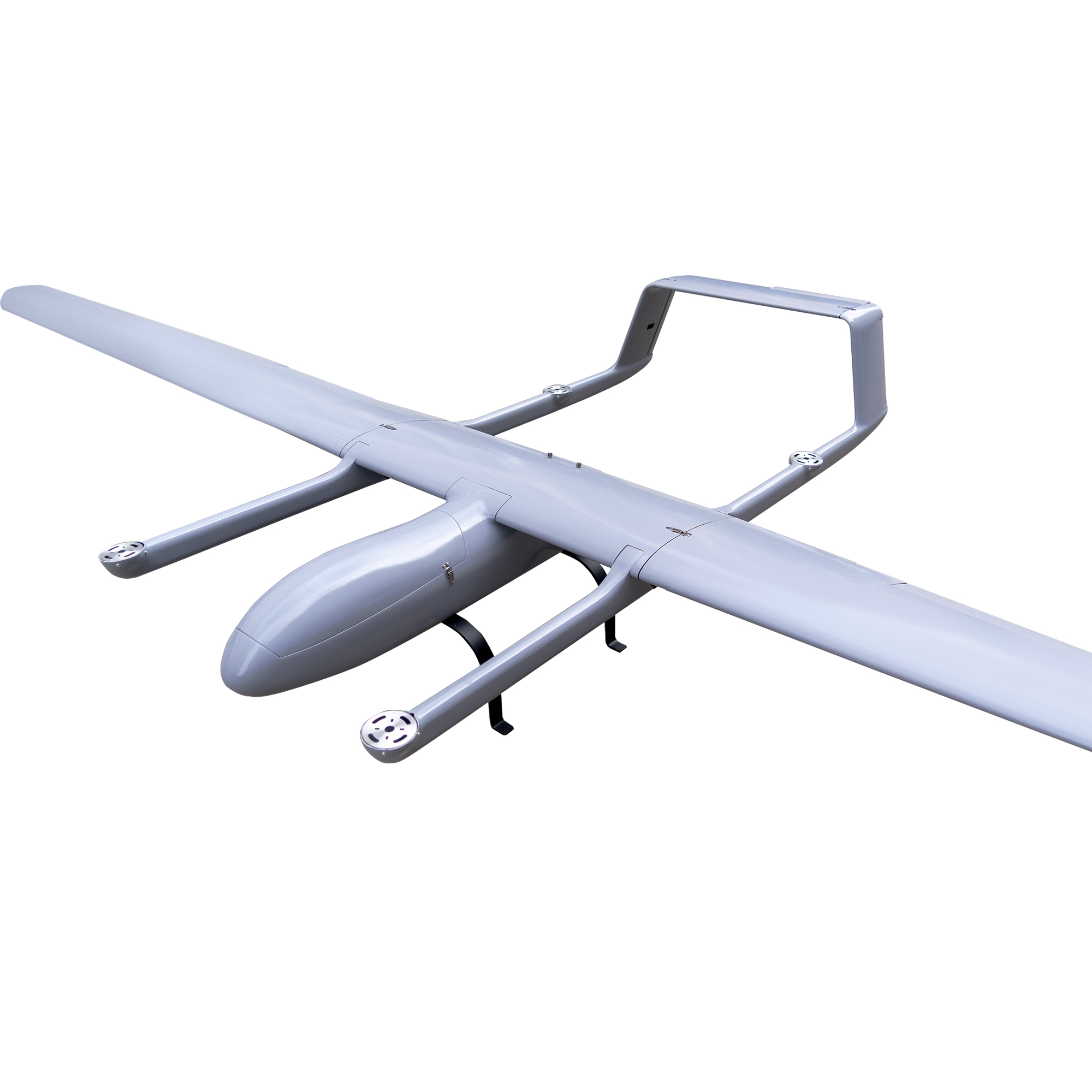
Mugin EV350M: Revolutionizing 3D Modeling with Advanced Mapping Capabilities
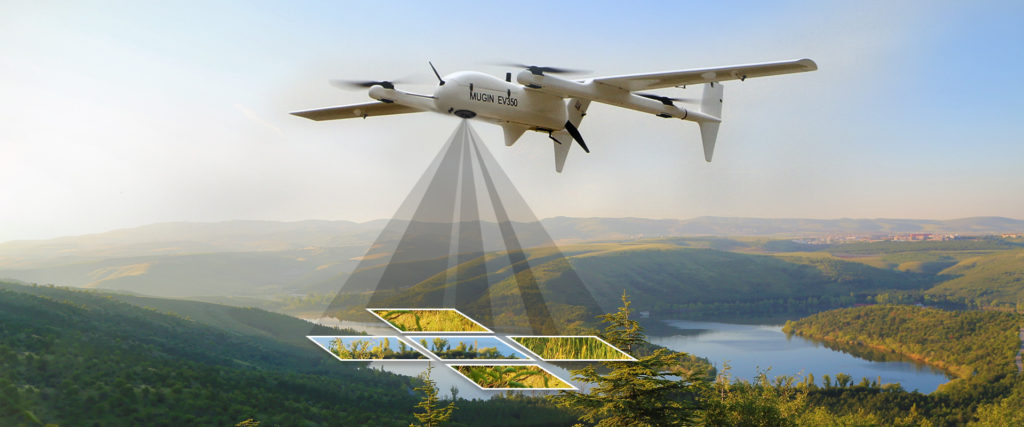

The Mugin EV350M is a cutting-edge electric mapping drone that comes equipped with a professional 5-lens oblique camera. This drone is an evolution of the EV350, specifically tailored for mapping and surveying purposes. The 5-lens oblique camera is instrumental in constructing detailed, centimeter-accurate geo-referenced maps, offering a comprehensive real-world view that aids in swift decision-making and project progress analysis.
The EV350M’s capabilities are not just limited to its camera. The drone itself is designed for safety and efficiency. With the EV350M, there’s no longer a need for personnel to traverse dangerous terrains or work at elevated heights; the drone can handle these tasks with ease. The data collected can be seamlessly processed through drone mapping software, resulting in assets like 3D models, 2D maps, and digital elevation models. These assets are invaluable for extracting critical information, such as precise measurements and volumetric calculations.
Key Features of the Mugin EV350M:
- Fast & Efficient Mapping: The drone can fly at speeds of 21 m/s, covering large areas in a single flight, making it up to 8 times faster than multicopter drones and twice as fast as other fixed-wing drones.
- High-Quality Imaging: With a 120 MP camera, the EV350M captures detailed images, ensuring more ground coverage and detail in every shot.
- Precision & Accuracy: The onboard high-precision PPK GNSS receiver, combined with 16-bit image processing technology, ensures clear, undistorted images, even in low-light conditions.
- Intelligent Interaction: The drone offers real-time viewing of camera ID, photo count, and camera status, ensuring smooth operations during flights.
- Lidar Range Sensor: The built-in Lidar range sensor offers accurate altitude measurements, aiding in automated landings, precise hovering, and terrain following.
Given its advanced features, the Mugin EV350M stands out as a premier tool for professionals in the 3D modeling domain. Its ability to capture high-resolution images from various angles, combined with its extended flight time and stability, ensures that the data collected is of the highest quality, making the process of 3D modeling more accurate and efficient.
Conclusion
Drone aerial photography and 3D modeling offer a powerful tool for a wide range of applications, from geological exploration to cultural heritage preservation. By capturing high-resolution images and processing them to create detailed 3D models, researchers and professionals can gain valuable insights and make informed decisions in their respective fields. As drone technology continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative applications and breakthroughs in the future.